Liquid-liquid phase separation in neuronal development and synaptic signaling
2020.10.12Wu, X., Cai, Q., Feng, Z., & Zhang, M. (2020). Developmental cell, 55(1), 18-29.
Formation of biomolecular condensates that are not enclosed by membranes via liquid-liquid phase separation (LLPS) is a general strategy that cells adopt to organize membraneless subcellular compartments for diverse functions. Neurons are highly polarized with elaborate branching and functional compartmentalization of their neurites, thus, raising additional demand for the proper subcellular localization of both membraneless and membrane-based organelles. Recent studies have provided evidence that several protein assemblies involved in the establishment of neuronal stem cell (NSC) polarity and in the asymmetric division of NSCs form distinct molecular condensates via LLPS. In synapses of adult neurons, molecular apparatuses controlling presynaptic neurotransmitter release and postsynaptic signaling transmission are also likely formed via LLPS. These molecular condensates, though not enclosed by lipid bilayers, directly associate with plasma membranes or membrane-based organelles, indicating that direct communication between membraneless and membrane-based organelles is a common theme in neurons and other types of cells.
- Recommend
-
2025-10-22
IQSEC2/BRAG1 may modulate postsynaptic density assembly through Ca2+-induced phase separation.
-
2025-08-22
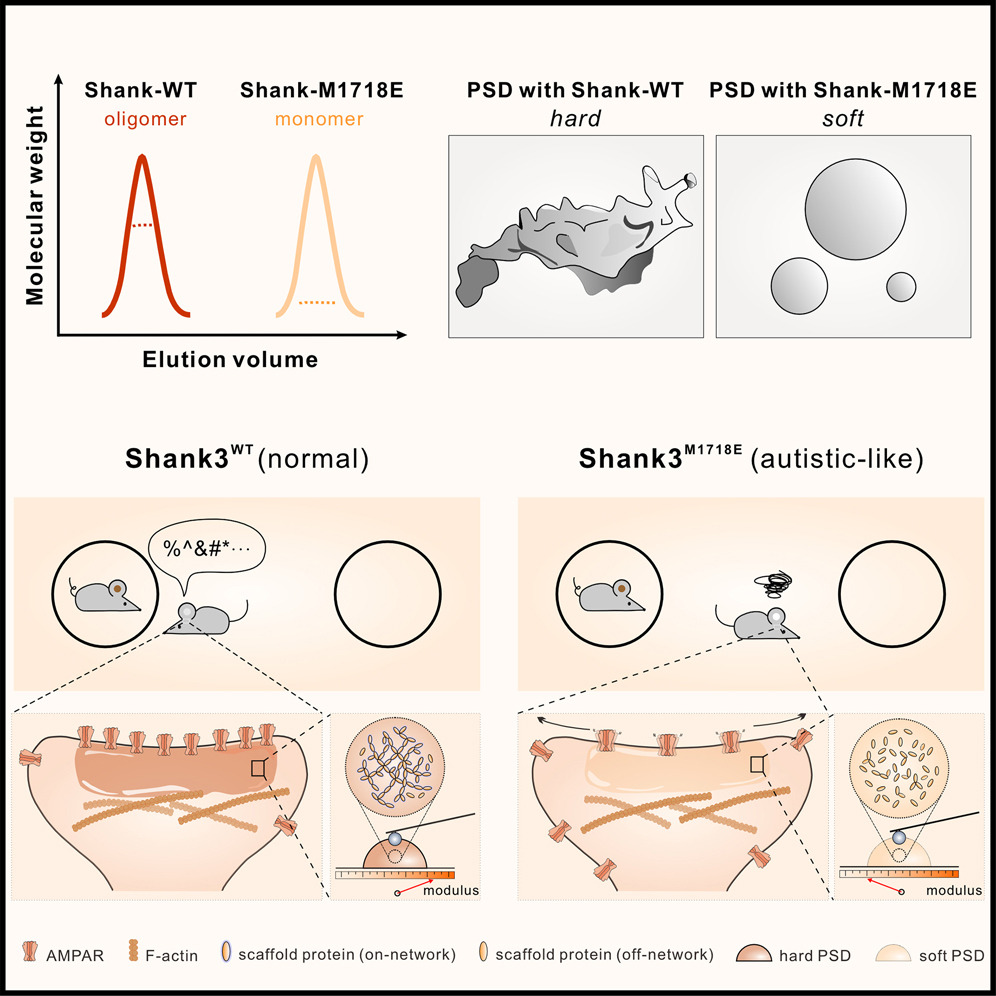
Shank3 oligomerization governs material properties of the postsynaptic density condensate and synaptic plasticity.
-
2025-08-21
Modulating synaptic glutamate receptors by targeting network nodes of the postsynaptic density condensate.
-
2025-08-19
Current practices in the study of biomolecular condensates: a community comment.
-
2025-06-10
Phase separation instead of binding strength determines target specificities of MAGUKs.