Gephyrin-mediated formation of inhibitory postsynaptic density sheet via phase separation
2020.11.02Bai, G., Wang, Y., & Zhang, M. (2021).Cell research, 31(3), 312-325.
Inhibitory synapses are also known as symmetric synapses due to their lack of prominent postsynaptic densities (PSDs) under a conventional electron microscope (EM). Recent cryo-EM tomography studies indicated that inhibitory synapses also contain PSDs, albeit with a rather thin sheet-like structure. It is not known how such inhibitory PSD (iPSD) sheet might form. Here, we demonstrate that the key inhibitory synapse scaffold protein gephyrin, when in complex with either glycine or GABAA receptors, spontaneously forms highly condensed molecular assemblies via phase separation both in solution and on supported membrane bilayers. Multivalent and specific interactions between the dimeric E-domain of gephyrin and the glycine/GABAA receptor multimer are essential for the iPSD condensate formation. Gephyrin alone does not form condensates. The linker between the G- and E-domains of gephyrin inhibits the iPSD condensate formation via autoinhibition. Phosphorylation of specific residues in the linker or binding of target proteins such as dynein light chain to the linker domain regulates gephyrin-mediated glycine/GABAA receptor clustering. Thus, analogous to excitatory PSDs, iPSDs are also formed by phase separation-mediated condensation of scaffold protein/neurotransmitter receptor complexes.
- Recommend
-
2025-10-22
IQSEC2/BRAG1 may modulate postsynaptic density assembly through Ca2+-induced phase separation.
-
2025-08-22
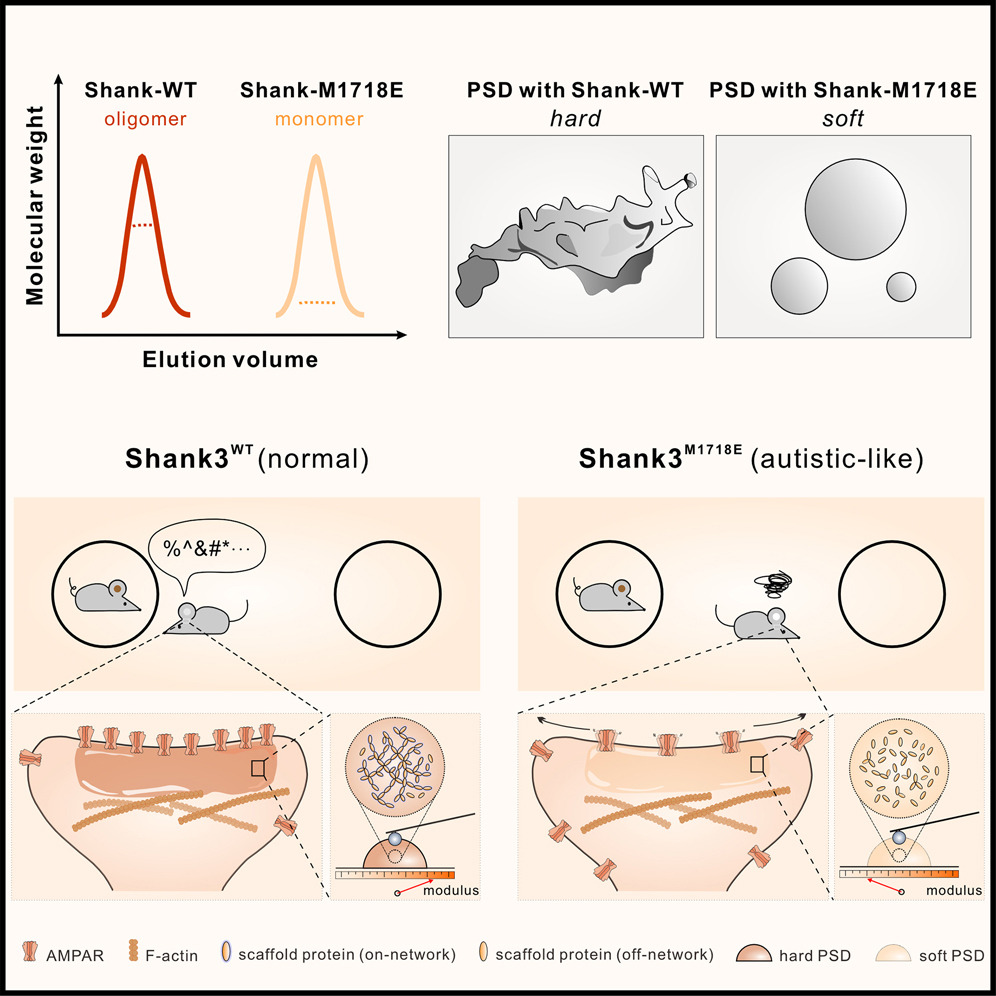
Shank3 oligomerization governs material properties of the postsynaptic density condensate and synaptic plasticity.
-
2025-08-21
Modulating synaptic glutamate receptors by targeting network nodes of the postsynaptic density condensate.
-
2025-08-19
Current practices in the study of biomolecular condensates: a community comment.
-
2025-06-10
Phase separation instead of binding strength determines target specificities of MAGUKs.