Structural basis of cargo recognitions for class V myosins
2013.06.24Wei, Z., Liu, X., Yu, C., & Zhang, M. (2013). Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 110(28), 11314-11319.
Class V myosins (MyoV), the most studied unconventional myosins, recognize numerous cargos mainly via the motor’s globular tail domain (GTD). Little is known regarding how MyoV-GTD recognizes such a diverse array of cargos specifically. Here, we solved the crystal structures of MyoVa-GTD in its apo-form and in complex with two distinct cargos, melanophilin and Rab interacting lysosomal protein-like 2. The apo-MyoVa-GTD structure indicates that most mutations found in patients with Griscelli syndrome, microvillus inclusion disease, or cancers or in “dilute” rodents likely impair the folding of GTD. The MyoVa-GTD/cargo complex structure reveals two distinct cargo-binding surfaces, one primarily via charge–charge interaction and the other mainly via hydrophobic interactions. Structural and biochemical analysis reveal the specific cargo-binding specificities of various isoforms of mammalian MyoV as well as very different cargo recognition mechanisms of MyoV between yeast and higher eukaryotes. The MyoVa-GTD structures resolved here provide a framework for future functional studies of vertebrate class V myosins.
- Recommend
-
2025-10-22
IQSEC2/BRAG1 may modulate postsynaptic density assembly through Ca2+-induced phase separation.
-
2025-08-22
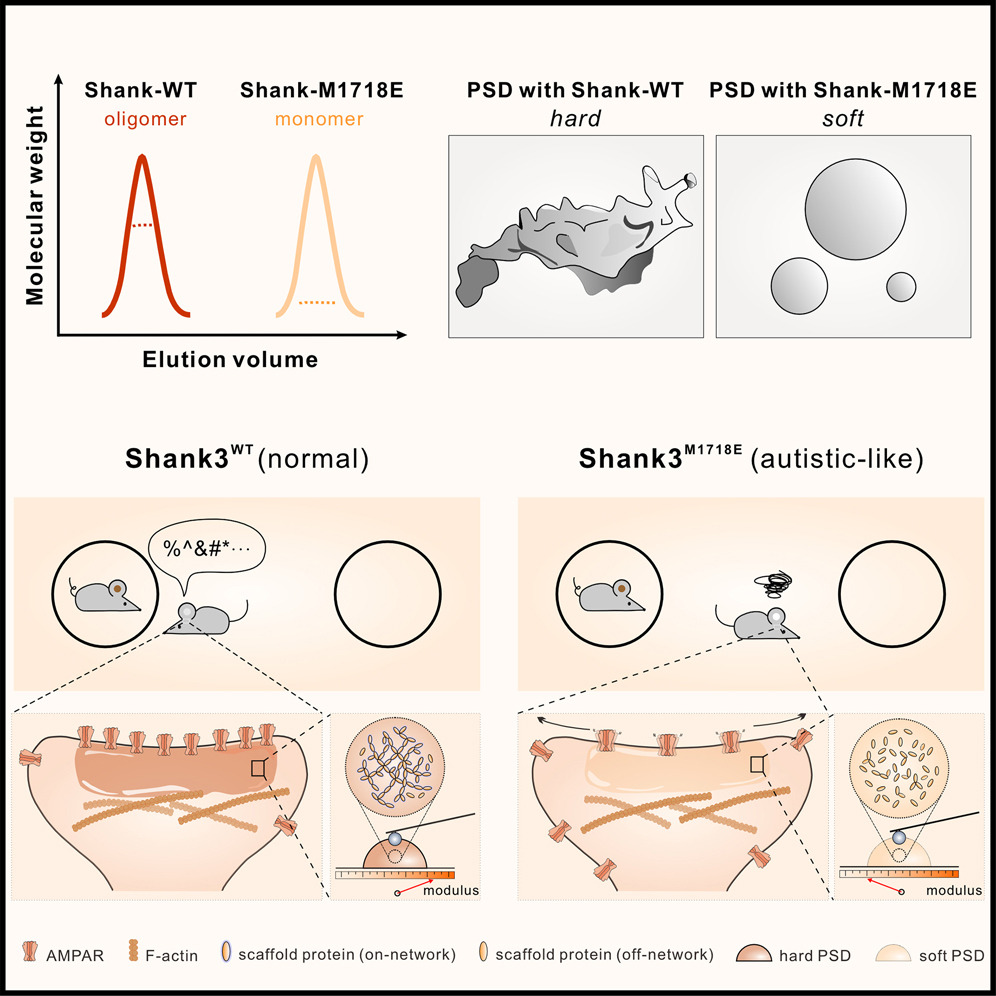
Shank3 oligomerization governs material properties of the postsynaptic density condensate and synaptic plasticity.
-
2025-08-21
Modulating synaptic glutamate receptors by targeting network nodes of the postsynaptic density condensate.
-
2025-08-19
Current practices in the study of biomolecular condensates: a community comment.
-
2025-06-10
Phase separation instead of binding strength determines target specificities of MAGUKs.