Regulated capture by exosomes of mRNAs for cytoplasmic tRNA synthetases
2013.09.03Wang, F., Xu, Z., Zhou, J., Lo, W. S., Lau, C. F., Nangle, L. A., ... Zhang, M., & Schimmel, P. (2013). Journal of Biological Chemistry, 288(41), 29223-29228.
Although tRNA synthetases are enzymes that catalyze the first step of translation in the cytoplasm, surprising functions unrelated to translation have been reported. These studies, and the demonstration of novel activities of splice variants, suggest a far broader reach of tRNA synthetases into cell biology than previously recognized. Here we show that mRNAs for most tRNA synthetases can be detected in exosomes. Also detected in exosomes was an mRNA encoding a unique splice variant that others had associated with prostate cancer. The exosomal mRNAs encoding the native synthetase and its cancer-associated splice variant could be translated in vitro and in mammalian cells into stable proteins. Other results showed that selection by exosomes of the splice variant mRNA could be regulated by an external stimulus. Thus, a broad and diverse regulated pool of tRNA synthetase-derived mRNAs is packaged for genetic exchange.
- Recommend
-
2025-10-22
IQSEC2/BRAG1 may modulate postsynaptic density assembly through Ca2+-induced phase separation.
-
2025-08-22
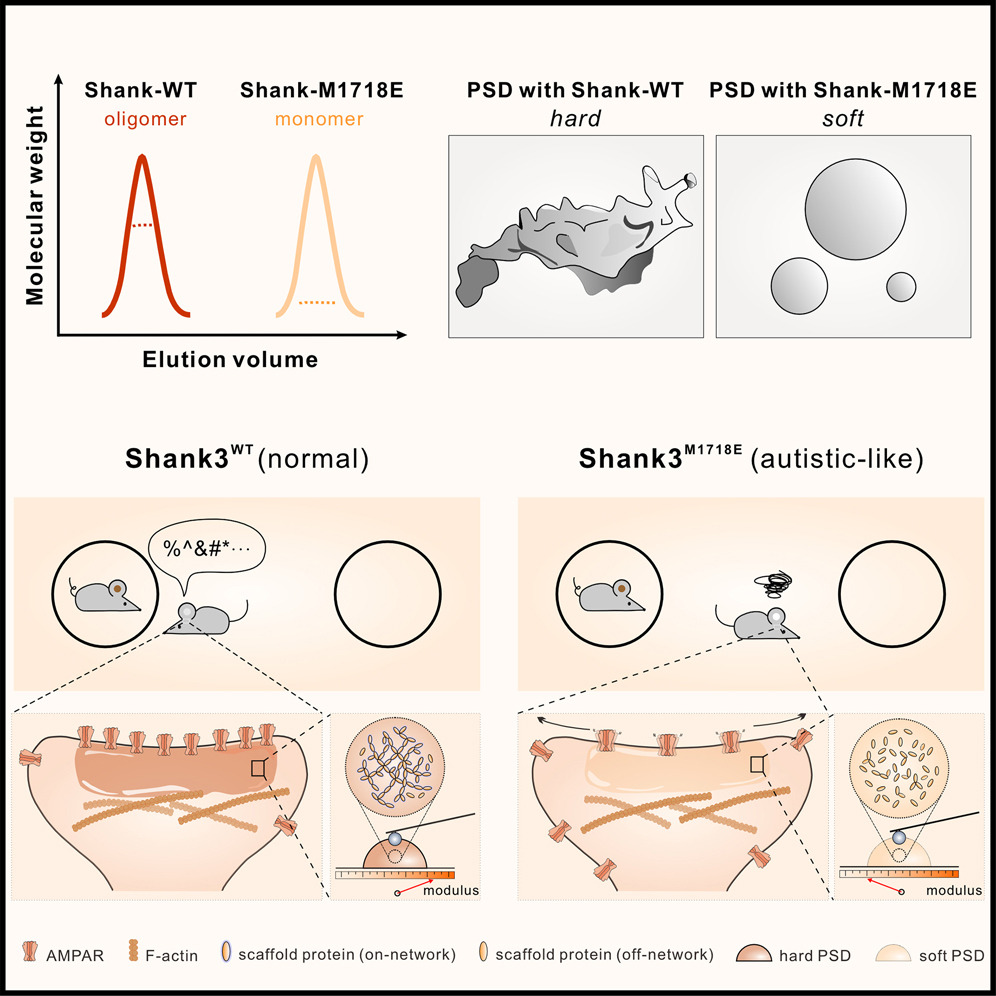
Shank3 oligomerization governs material properties of the postsynaptic density condensate and synaptic plasticity.
-
2025-08-21
Modulating synaptic glutamate receptors by targeting network nodes of the postsynaptic density condensate.
-
2025-08-19
Current practices in the study of biomolecular condensates: a community comment.
-
2025-06-10
Phase separation instead of binding strength determines target specificities of MAGUKs.