Mechanisms of MAGUK-mediated cellular junctional complex organization
2018.04.01Ye, F., Zeng, M., & Zhang, M. (2018). Current Opinion in Structural Biology, 48, 6-15.
Membrane-associated guanylate kinases (MAGUKs) are a family of scaffold proteins that are enriched in cellular junctions and essential for tissue development and homeostasis. Mutations of MAGUKs are linked to many human diseases including cancers, psychiatric disorders, and intellectual disabilities. MAGUKs share a common PDZ-SH3-GK tandem domain organization at the C-terminal end. In this review, we summarize the mechanistic basis governing target recognition and regulations of this binding by the PDZ-SH3-GK tandem of various MAGUKs. We also discuss recent discoveries showing unique folding features of MAGUK PDZ-SH3-GK tandems that facilitate ligand-induced oligomerization of MAGUKs and phase transition of MAGUK-assembled synaptic signaling complexes.
- Recommend
-
2025-10-22
IQSEC2/BRAG1 may modulate postsynaptic density assembly through Ca2+-induced phase separation.
-
2025-08-22
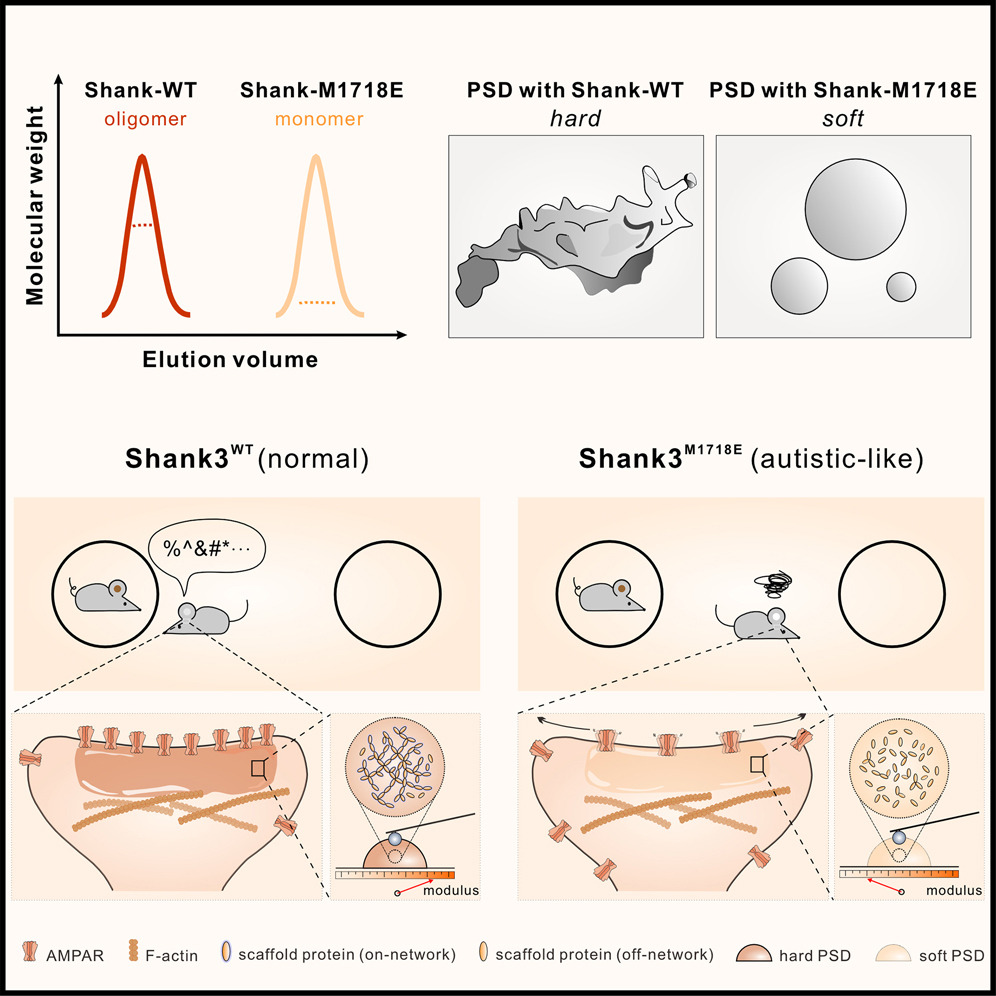
Shank3 oligomerization governs material properties of the postsynaptic density condensate and synaptic plasticity.
-
2025-08-21
Modulating synaptic glutamate receptors by targeting network nodes of the postsynaptic density condensate.
-
2025-08-19
Current practices in the study of biomolecular condensates: a community comment.
-
2025-06-10
Phase separation instead of binding strength determines target specificities of MAGUKs.