Basal condensation of Numb and Pon complex via phase transition during Drosophila neuroblast asymmetric division
2018.02.21Shan, Z., Tu, Y., Yang, Y., Liu, Z., Zeng, M., Xu, H., Long, J., Zhang, M., Cai, Y. and Wen, W.(2018). Nature Communications, 9, 737.
Uneven distribution and local concentration of protein complexes on distinct membrane cortices is a fundamental property in numerous biological processes, including Drosophila neuroblast (NB) asymmetric cell divisions and cell polarity in general. In NBs, the cell fate determinant Numb forms a basal crescent together with Pon and is segregated into the basal daughter cell to initiate its differentiation. Here we discover that Numb PTB domain, using two distinct binding surfaces, recognizes repeating motifs within Pon in a previously unrecognized mode. The multivalent Numb-Pon interaction leads to high binding specificity and liquid-liquid phase separation of the complex. Perturbations of the Numb/Pon complex phase transition impair the basal localization of Numb and its subsequent suppression of Notch signaling during NB asymmetric divisions. Such phase-transition-mediated protein condensations on distinct membrane cortices may be a general mechanism for various cell polarity regulatory complexes.
- Recommend
-
2025-10-22
IQSEC2/BRAG1 may modulate postsynaptic density assembly through Ca2+-induced phase separation.
-
2025-08-22
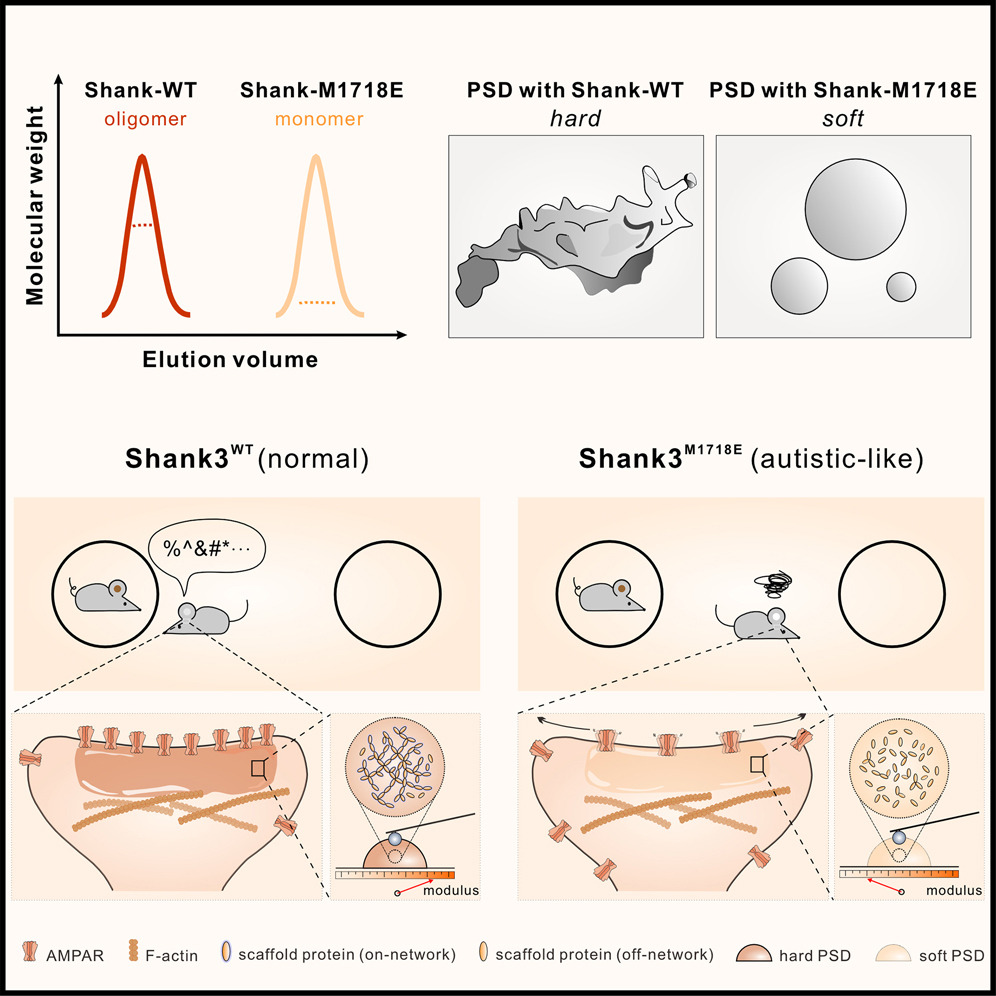
Shank3 oligomerization governs material properties of the postsynaptic density condensate and synaptic plasticity.
-
2025-08-21
Modulating synaptic glutamate receptors by targeting network nodes of the postsynaptic density condensate.
-
2025-08-19
Current practices in the study of biomolecular condensates: a community comment.
-
2025-06-10
Phase separation instead of binding strength determines target specificities of MAGUKs.