Large protein assemblies formed by multivalent interactions between cadherin23 and harmonin suggest a stable anchorage structure at the tip link of stereocilia
2012.08.08Wu, L., Pan, L., Zhang, C., & Zhang, M. (2012). Journal of Biological Chemistry, 287(40), 33460-33471.
Stereocilia tip links of inner ear hair cells are subjected to constant stretching during hair-bundle deflection, and accordingly are well designed to prevent from being broken by mechanical tensions. The roots of tip links, which couple tip links with the cytoskeleton, supposedly play important roles in withstanding large forces under stimulated conditions. The upper root of the tip link is mainly formed by the cytoplasmic tail of cadherin23 and its actin-anchoring protein harmonin. However, the detailed organization mode of the two proteins that gives rise to a strong upper root remains unclear. Here we show that the exon68-encoded peptide of cadherin23 can either interact with the N-terminal domain (NTD) of harmonin or form a homodimer. We demonstrate that the three harmonin binding sites of cadherin23, namely the NTD-binding motif, the exon68 peptide, and the C-terminal PDZ binding motif, do not synergize with each other in binding to harmonin, instead they facilitate formation of polymeric cadherin23/harmonin complexes. The exon68 peptide can promote the cadherin23/harmonin polymer formation via either binding to harmonin NTD or self-dimerization. We propose that the polymeric cadherin23/harmonin complex formed beneath the upper tip link membranes may serve as part of the stable rootlet structure for anchoring the tip links of stereocilia.
- Recommend
-
2025-10-22
IQSEC2/BRAG1 may modulate postsynaptic density assembly through Ca2+-induced phase separation.
-
2025-08-22
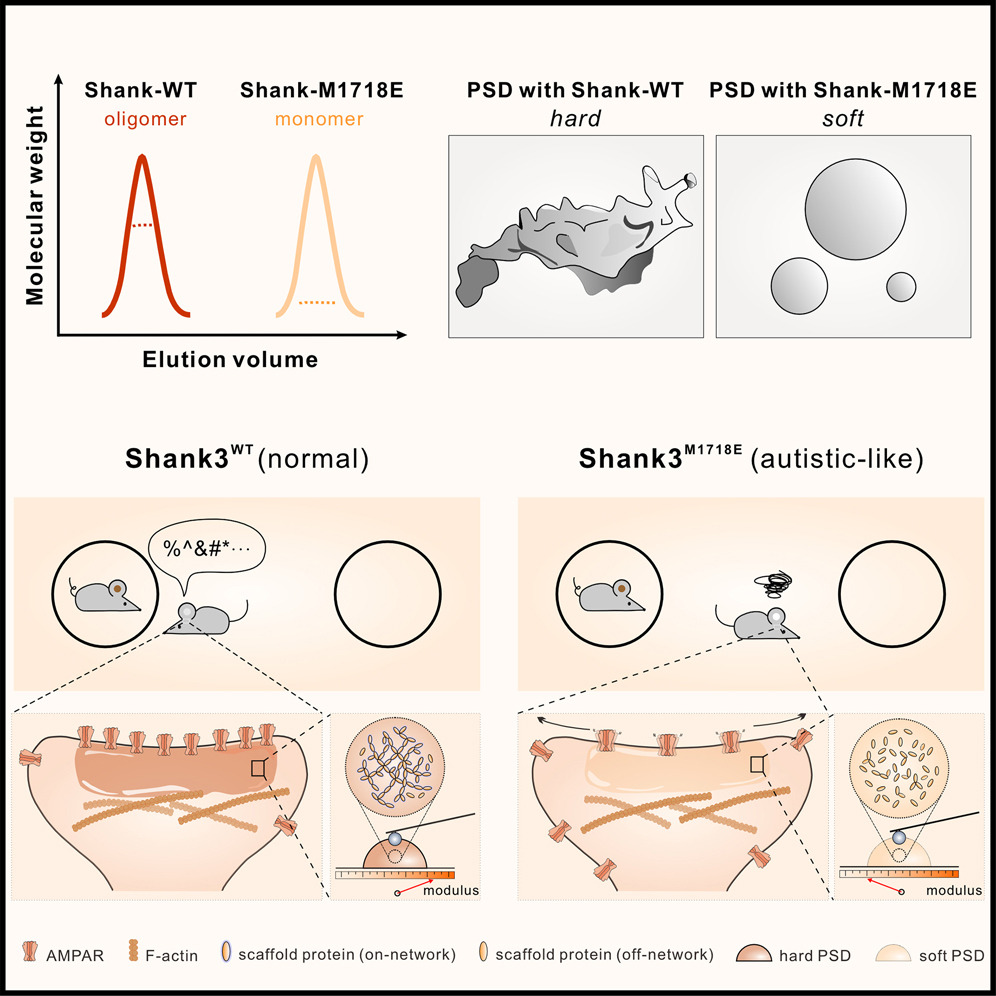
Shank3 oligomerization governs material properties of the postsynaptic density condensate and synaptic plasticity.
-
2025-08-21
Modulating synaptic glutamate receptors by targeting network nodes of the postsynaptic density condensate.
-
2025-08-19
Current practices in the study of biomolecular condensates: a community comment.
-
2025-06-10
Phase separation instead of binding strength determines target specificities of MAGUKs.