Regulation of microtubule stability and organization by mammalian Par3 in specifying neuronal polarity
2013.01.14Chen, S., Chen, J., Shi, H., Wei, M., Castaneda-Castellanos, D. R., Bultje, R. S., Zhang, M., ... & Shi, S. H. (2013). Developmental cell, 24(1), 26-40.
Polarization of mammalian neurons with a specified axon requires precise regulation of microtubule and actin dynamics in the developing neurites. Here we show that mammalian partition defective 3 (mPar3), a key component of the Par polarity complex that regulates the polarization of many cell types including neurons, directly regulates microtubule stability and organization. The N-terminal portion of mPar3 exhibits strong microtubule binding, bundling, and stabilization activity, which can be suppressed by its C-terminal portion via an intramolecular interaction. Interestingly, the intermolecular oligomerization of mPar3 is able to relieve the intramolecular interaction and thereby promote microtubule bundling and stabilization. Furthermore, disruption of this microtubule regulatory activity of mPar3 impairs its function in axon specification. Together, these results demonstrate a role for mPar3 in directly regulating microtubule organization that is crucial for neuronal polarization.
- Recommend
-
2025-10-22
IQSEC2/BRAG1 may modulate postsynaptic density assembly through Ca2+-induced phase separation.
-
2025-08-22
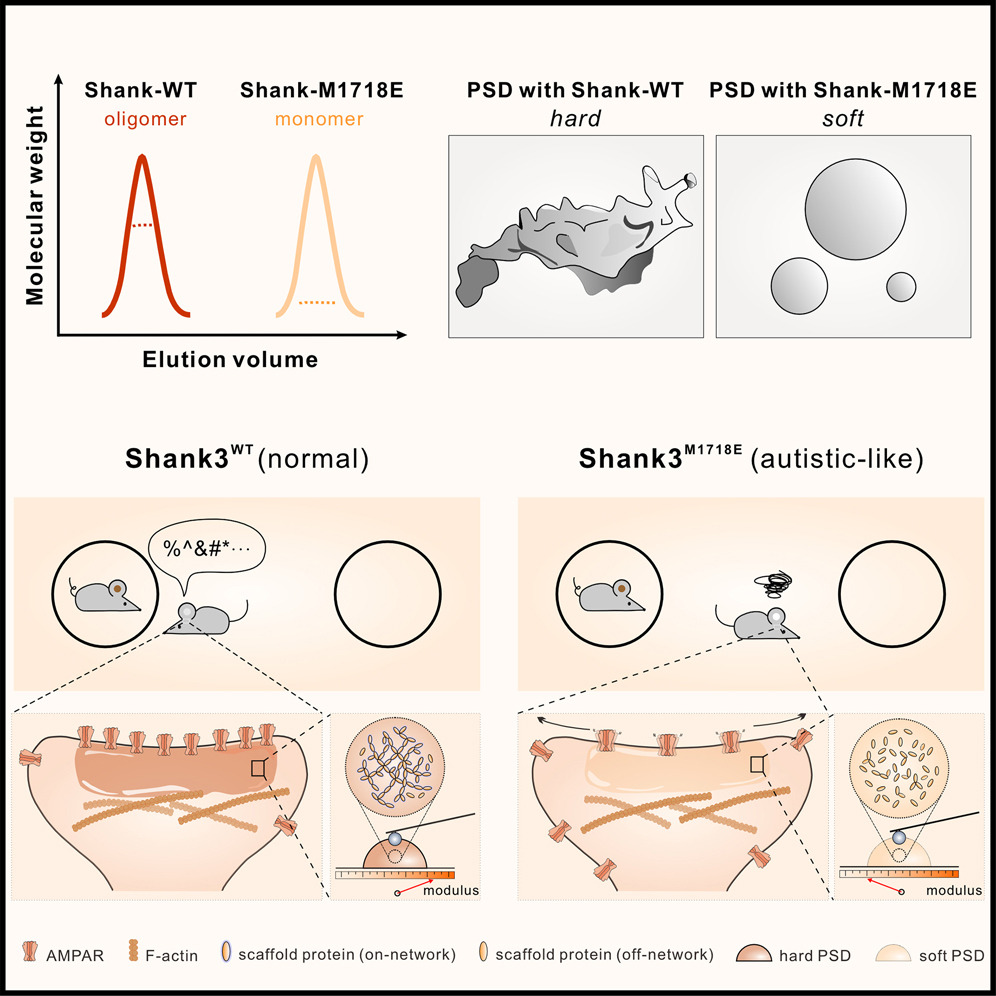
Shank3 oligomerization governs material properties of the postsynaptic density condensate and synaptic plasticity.
-
2025-08-21
Modulating synaptic glutamate receptors by targeting network nodes of the postsynaptic density condensate.
-
2025-08-19
Current practices in the study of biomolecular condensates: a community comment.
-
2025-06-10
Phase separation instead of binding strength determines target specificities of MAGUKs.