An autoinhibited conformation of LGN reveals a distinct interaction mode between GoLoco motifs and TPR motifs
2013.06.04Pan, Z., Zhu, J., Shang, Y., Wei, Z., Jia, M., Xia, C., ... & Zhang, M. (2013). Structure, 21(6), 1007-1017.
LGN plays essential roles in asymmetric cell divisions via its N-terminal TPR-motif-mediated binding to mInsc and NuMA. This scaffolding activity requires the release of the autoinhibited conformation of LGN by binding of Gαi to its C-terminal GoLoco (GL) motifs. The interaction between the GL and TPR motifs of LGN represents a distinct GL/target binding mode with an unknown mechanism. Here, we show that two consecutive GL motifs of LGN form a minimal TPR-motif-binding unit. GL12 and GL34 bind to TPR0–3 and TPR4–7, respectively. The crystal structure of a truncated LGN reveals that GL34 forms a pair of parallel α helices and binds to the concave surface of TPR4–7, thereby preventing LGN from binding to other targets. Importantly, the GLs bind to TPR motifs with a mode distinct from that observed in the GL/Gαi·GDP complexes. Our results also indicate that multiple and orphan GL motif proteins likely respond to G proteins with distinct mechanisms.
- Recommend
-
2025-10-22
IQSEC2/BRAG1 may modulate postsynaptic density assembly through Ca2+-induced phase separation.
-
2025-08-22
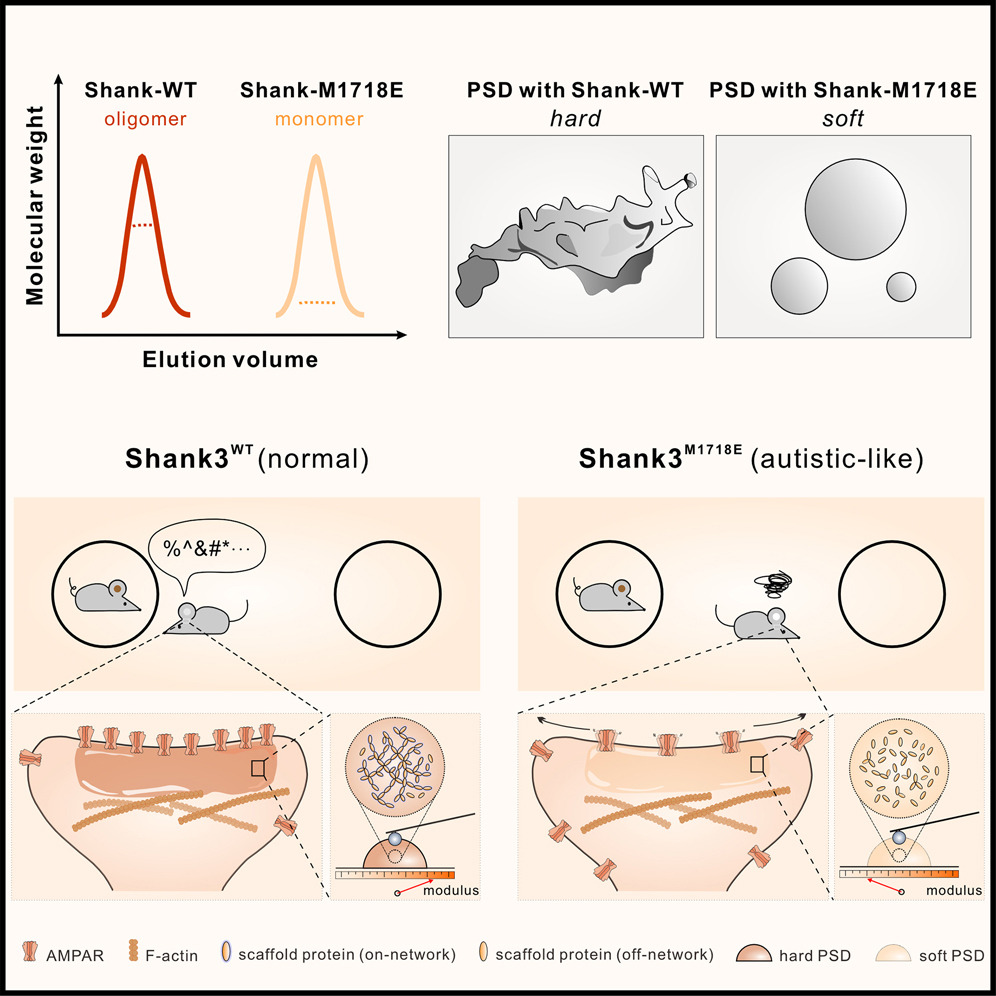
Shank3 oligomerization governs material properties of the postsynaptic density condensate and synaptic plasticity.
-
2025-08-21
Modulating synaptic glutamate receptors by targeting network nodes of the postsynaptic density condensate.
-
2025-08-19
Current practices in the study of biomolecular condensates: a community comment.
-
2025-06-10
Phase separation instead of binding strength determines target specificities of MAGUKs.