Angiomotin binding-induced activation of Merlin/NF2 in the Hippo pathway
2015.06.05Li, Y., Zhou, H., Li, F., Chan, S. W., Lin, Z., Wei, Z., ... & Zhang, M. (2015). Cell research, 25(7), 801-817.
The tumor suppressor Merlin/NF2 functions upstream of the core Hippo pathway kinases Lats1/2 and Mst1/2, as well as the nuclear E3 ubiquitin ligase CRL4DCAF1. Numerous mutations of Merlin have been identified in Neurofibromatosis type 2 and other cancer patients. Despite more than two decades of research, the upstream regulator of Merlin in the Hippo pathway remains unknown. Here we show by high-resolution crystal structures that the Lats1/2-binding site on the Merlin FERM domain is physically blocked by Merlin's auto-inhibitory tail. Angiomotin binding releases the auto-inhibition and promotes Merlin's binding to Lats1/2. Phosphorylation of Ser518 outside the Merlin's auto-inhibitory tail does not obviously alter Merlin's conformation, but instead prevents angiomotin from binding and thus inhibits Hippo pathway kinase activation. Cancer-causing mutations clustered in the angiomotin-binding domain impair angiomotin-mediated Merlin activation. Our findings reveal that angiomotin and Merlin respectively interface cortical actin filaments and core kinases in Hippo signaling, and allow construction of a complete Hippo signaling pathway.
- Recommend
-
2025-10-22
IQSEC2/BRAG1 may modulate postsynaptic density assembly through Ca2+-induced phase separation.
-
2025-08-22
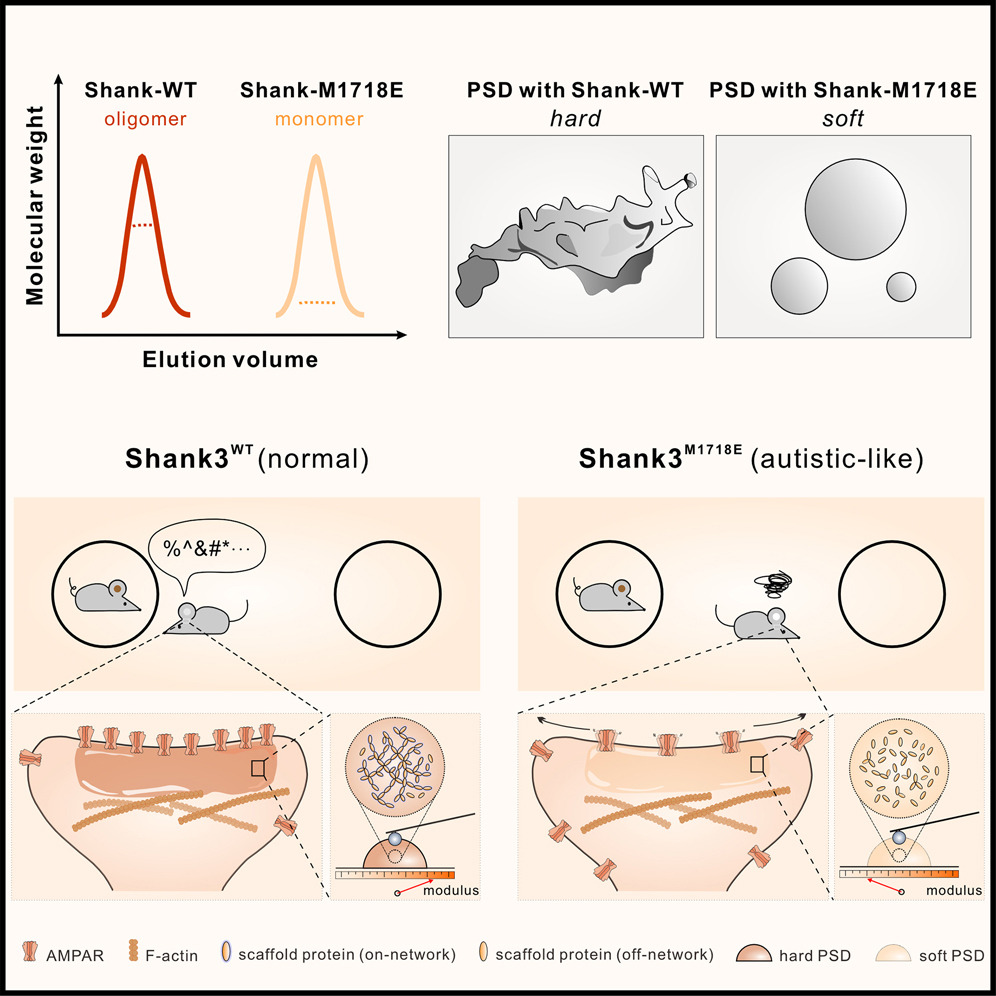
Shank3 oligomerization governs material properties of the postsynaptic density condensate and synaptic plasticity.
-
2025-08-21
Modulating synaptic glutamate receptors by targeting network nodes of the postsynaptic density condensate.
-
2025-08-19
Current practices in the study of biomolecular condensates: a community comment.
-
2025-06-10
Phase separation instead of binding strength determines target specificities of MAGUKs.