Myosin VII, USH1C, and ANKS4B or USH1G together form condensed molecular assembly via liquid-liquid phase separation
2019.10.22He, Y., Li, J., & Zhang, M. (2019). Cell reports, 29(4), 974-986.
Hair cell stereocilia tip-links function to sense mechanical forces generated by sound waves and maintain the structure of stereocilia by rooting the tail of cadherins to highly dense structures known as tip-link densities. Although the molecular components are largely known, the mechanisms underlying the tip-link density formation are unknown. Here, we show that Myosin VIIB (MYO7B), USH1C, and ANKS4B, which form a specific complex stabilizing tip-links in intestine microvilli, could form dense condensates via liquid-liquid phase separation in vitro and in cells. The MYO7A, USH1C, and USH1G complex also undergoes phase separation in cells. Formation of the MYO7A/USH1C/USH1G and MYO7B/USH1C/ANKS4B condensates requires strong and multivalent interactions between proteins in both tripartite complexes. Point mutations of MYO7A found in Usher syndrome patients weaken or even disrupt the multivalent interactions of the MYO7A/USH1C/USH1G complex and impair its phase separation. Thus, the stereocilia tip-link densities may form via phase separation of the MYO7A/USH1C/USH1G complex.
- Recommend
-
2025-10-22
IQSEC2/BRAG1 may modulate postsynaptic density assembly through Ca2+-induced phase separation.
-
2025-08-22
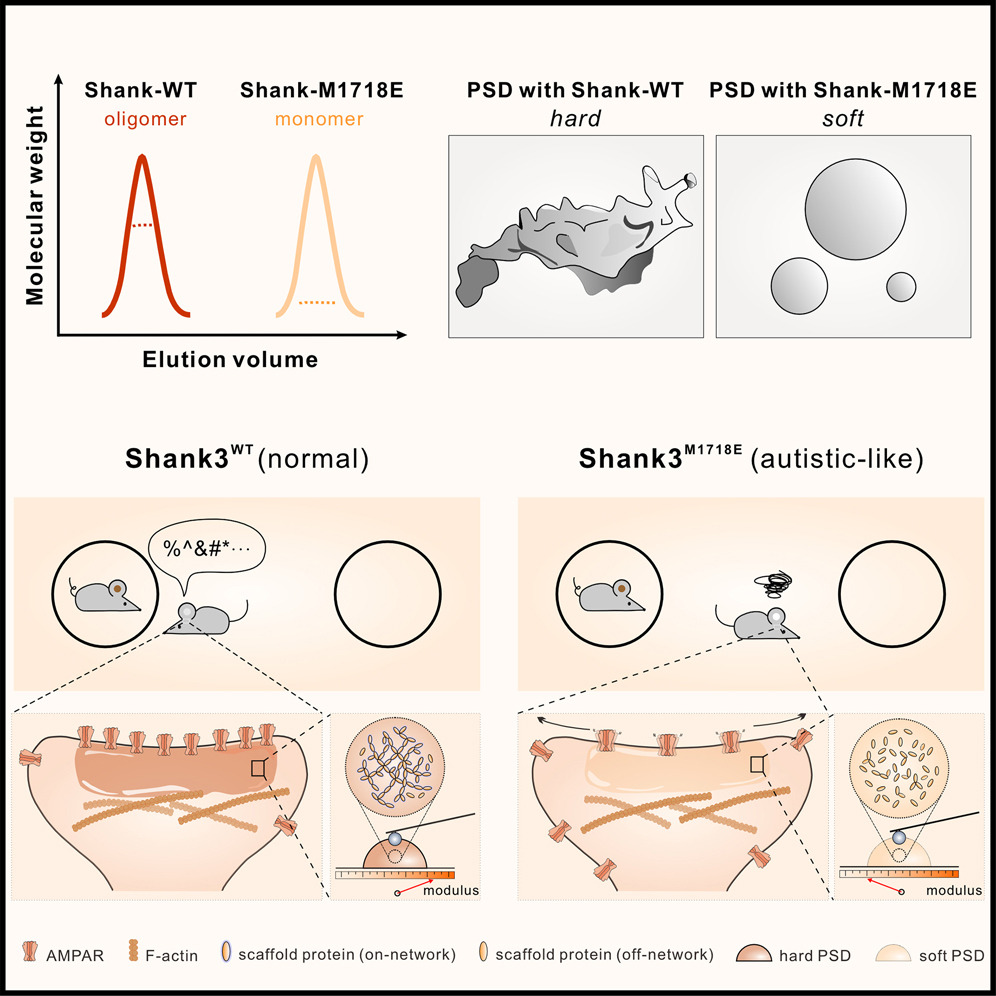
Shank3 oligomerization governs material properties of the postsynaptic density condensate and synaptic plasticity.
-
2025-08-21
Modulating synaptic glutamate receptors by targeting network nodes of the postsynaptic density condensate.
-
2025-08-19
Current practices in the study of biomolecular condensates: a community comment.
-
2025-06-10
Phase separation instead of binding strength determines target specificities of MAGUKs.