Liquid–liquid phase separation in biology: specific stoichiometric molecular interactions vs promiscuous interactions mediated by disordered sequences
2021.07.22Feng, Z., Jia, B., & Zhang, M. (2021). Biochemistry, 60(31), 2397-2406.
Extensive studies in the past few years have shown that nonmembrane bound organelles are likely assembled via liquid–liquid phase separation (LLPS), a process that is driven by multivalent protein–protein and/or protein–nucleic acid interactions. Both stoichiometric molecular interactions and intrinsically disordered region (IDR)-driven interactions can promote the assembly of membraneless organelles, and the field is currently dominated by IDR-driven biological condensate formation. Here we discuss recent studies that demonstrate the importance of specific biomolecular interactions for functions of diverse physiological condensates. We suggest that phase separation based on combinations of specific interactions and promiscuous IDR-driven interactions is likely a general feature of biological condensation under physiological conditions.
- Recommend
-
2025-10-22
IQSEC2/BRAG1 may modulate postsynaptic density assembly through Ca2+-induced phase separation.
-
2025-08-22
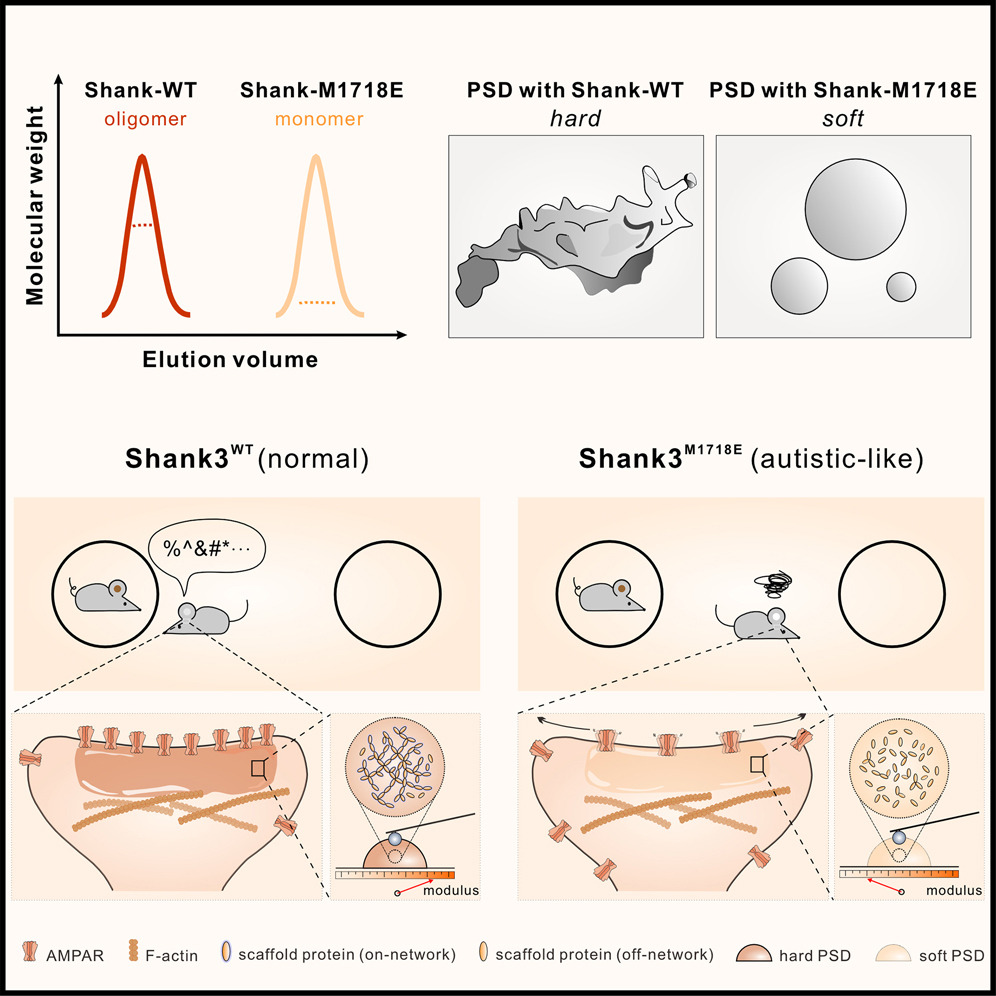
Shank3 oligomerization governs material properties of the postsynaptic density condensate and synaptic plasticity.
-
2025-08-21
Modulating synaptic glutamate receptors by targeting network nodes of the postsynaptic density condensate.
-
2025-08-19
Current practices in the study of biomolecular condensates: a community comment.
-
2025-06-10
Phase separation instead of binding strength determines target specificities of MAGUKs.