Cdc42‐dependent formation of the ZO‐1/MRCKβ complex at the leading edge controls cell migration
2011.01.14Huo, L., Wen, W., Wang, R., Kam, C., Xia, J., Feng, W., & Zhang, M. (2011). The EMBO journal, 30(4), 665-678.
Zonula occludens (ZO)-1 is a multi-domain scaffold protein known to have critical roles in the establishment of cell–cell adhesions and the maintenance of stable tissue structures through the targeting, anchoring, and clustering of transmembrane adhesion molecules and cytoskeletal proteins. Here, we report that ZO-1 directly binds to MRCKβ, a Cdc42 effector kinase that modulates cell protrusion and migration, at the leading edge of migrating cells. Structural studies reveal that the binding of a β hairpin from GRINL1A converts ZO-1 ZU5 into a complete ZU5-fold. A similar interaction mode is likely to occur between ZO-1 ZU5 and MRCKβ. The interaction between ZO-1 and MRCKβ requires the kinase to be primed by Cdc42 due to the closed conformation of the kinase. Formation of the ZO-1/MRCKβ complex enriches the kinase at the lamellae of migrating cells. Disruption of the ZO-1/MRCKβ complex inhibits MRCKβ-mediated cell migration. These results demonstrate that ZO-1, a classical scaffold protein with accepted roles in maintaining cell–cell adhesions in stable tissues, also has an active role in cell migration during processes such as tissue development and remodelling.
- Recommend
-
2025-10-22
IQSEC2/BRAG1 may modulate postsynaptic density assembly through Ca2+-induced phase separation.
-
2025-08-22
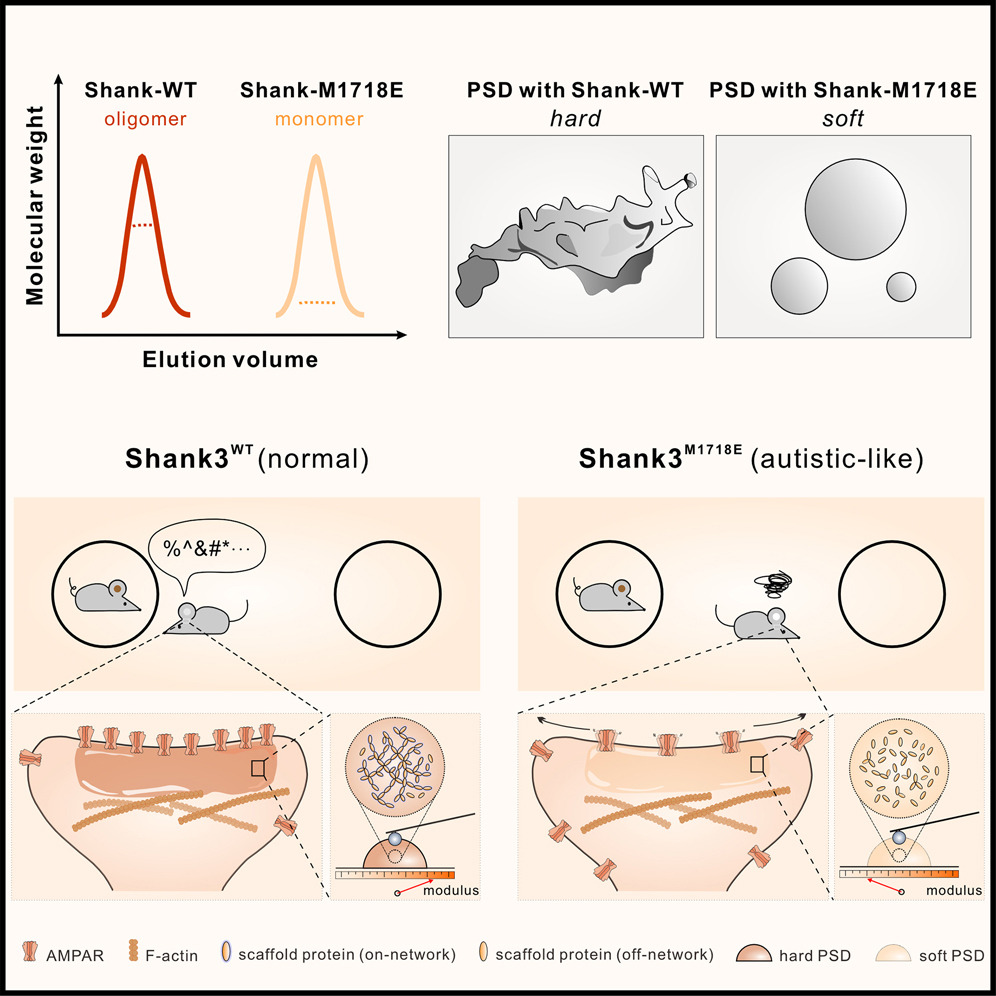
Shank3 oligomerization governs material properties of the postsynaptic density condensate and synaptic plasticity.
-
2025-08-21
Modulating synaptic glutamate receptors by targeting network nodes of the postsynaptic density condensate.
-
2025-08-19
Current practices in the study of biomolecular condensates: a community comment.
-
2025-06-10
Phase separation instead of binding strength determines target specificities of MAGUKs.