Structure and function of the guanylate kinase-like domain of the MAGUK family scaffold proteins
2012.10.11Zhu, J., Shang, Y., Chen, J., & Zhang, M. (2012). Frontiers in biology, 7, 379-396.
Membrane associated guanylate kinases (MAGUKs) are a family of scaffold proteins that play essential roles in organ development, cell-cell communication, cell polarity establishment and maintenance, and cellular signal transduction. Every member of the MAGUK family contains a guanylate kinase-like (GK) domain, which has evolved from the enzyme catalyzing GMP to GDP conversion to become a protein-protein interaction module with no enzymatic activity.Mutations of MAGUKs are linked to a number of human diseases, including autism and hereditary deafness. In this review, we summarize the structural basis governing cellular function of various members of the MAGUKs. In particular, we focus on recent discoveries of MAGUK GKs as specific phospho-protein interaction modules, and discuss functional implications and connections to human diseases of such regulated MAGUK GK/target interactions.
- Recommend
-
2025-10-22
IQSEC2/BRAG1 may modulate postsynaptic density assembly through Ca2+-induced phase separation.
-
2025-08-22
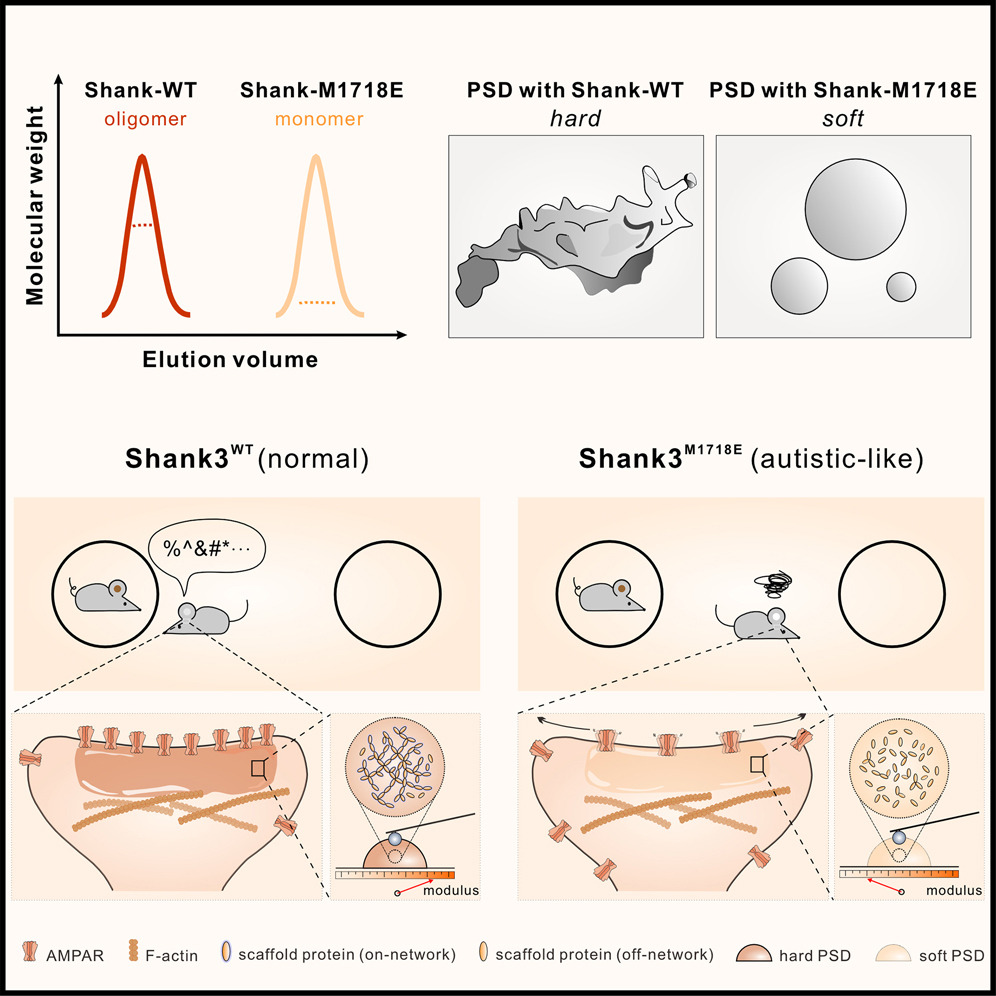
Shank3 oligomerization governs material properties of the postsynaptic density condensate and synaptic plasticity.
-
2025-08-21
Modulating synaptic glutamate receptors by targeting network nodes of the postsynaptic density condensate.
-
2025-08-19
Current practices in the study of biomolecular condensates: a community comment.
-
2025-06-10
Phase separation instead of binding strength determines target specificities of MAGUKs.