Kibra modulates learning and memory via binding to dendrin
2019.04.19Ji, Z., Li, H., Yang, Z., Huang, X., Ke, X., Ma, S., ... & Zhang, M. (2019). Cell reports, 26(8), 2064-2077.
Kibra is a synaptic scaffold protein regulating learning and memory. Alterations of Kibra-encoding gene WWC1 cause various neuronal disorders, including Alzheimer’s disease and Tourette syndrome. However, the molecular mechanism underlying Kibra’s function in neurons is poorly understood. Here we discover that Kibra, via its N-terminal WW12 tandem domains, binds to a postsynaptic density enriched protein, Dendrin, with a nanomolar dissociation constant. On the basis of the structure of Kibra WW12 in complex with Dendrin PY motifs, we developed a potent peptide inhibitor capable of specifically blocking the binding between Kibra and Dendrin in neurons. Systematic administration of the inhibitory peptide attenuated excitatory synaptic transmission, completely blocked long-term potentiation induction, and impaired spatial learning and memory. A Kibra mutation found in Tourette syndrome patients causes defects in binding to Dendrin. Thus, Kibra can modulate spatial learning and memory via binding to Dendrin.
- Recommend
-
2025-10-22
IQSEC2/BRAG1 may modulate postsynaptic density assembly through Ca2+-induced phase separation.
-
2025-08-22
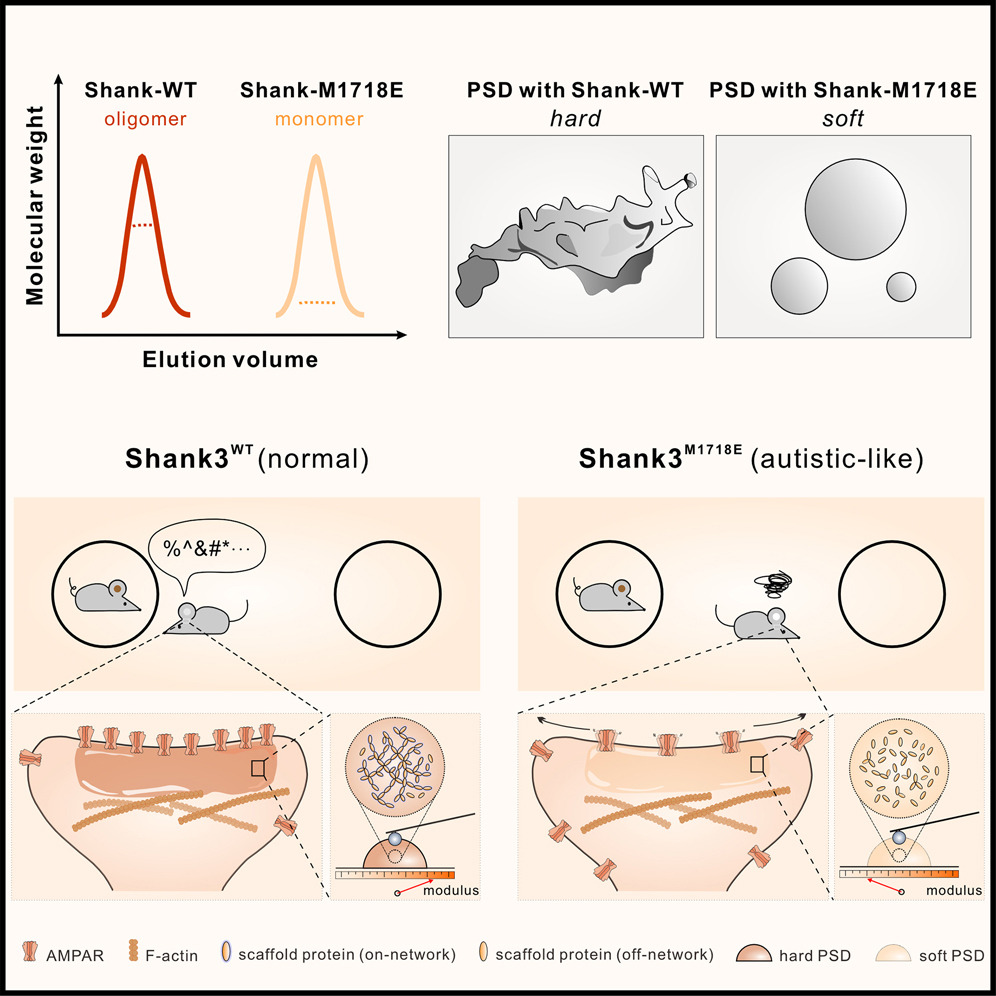
Shank3 oligomerization governs material properties of the postsynaptic density condensate and synaptic plasticity.
-
2025-08-21
Modulating synaptic glutamate receptors by targeting network nodes of the postsynaptic density condensate.
-
2025-08-19
Current practices in the study of biomolecular condensates: a community comment.
-
2025-06-10
Phase separation instead of binding strength determines target specificities of MAGUKs.