Shank3 binds to and stabilizes the active form of Rap1 and HRas GTPases via Its NTD-ANK tandem with distinct mechanisms
2020.03.03Cai, Q., Hosokawa, T., Zeng, M., Hayashi, Y., & Zhang, M. (2020). Structure, 28(3), 290-300.
Shank1/2/3, major scaffold proteins in excitatory synapses, are frequently mutated in patients with psychiatric disorders. Although the Shank N-terminal domain and ankyrin repeats domain tandem (NTD-ANK) is known to bind to Ras and Rap1, the molecular mechanism underlying and functional significance of the bindings in synapses are unknown. Here, we demonstrate that Shank3 NTD-ANK specifically binds to the guanosine triphosphate (GTP)-bound form of HRas and Rap1. In addition to the canonical site mediated by the Ras-association domain and common to both GTPases, Shank3 contains an unconventional Rap1 binding site formed by NTD and ANK together. Binding of Shank3 to the GTP-loaded Rap1 slows down its GTP hydrolysis by SynGAP. We further show that the interactions between Shank3 and HRas/Rap1 at excitatory synapses are promoted by synaptic activation. Thus, Shank3 may be able to modulate signaling of the Ras family proteins via directly binding to and stabilizing the GTP-bound form of the enzymes.
- Recommend
-
2025-10-22
IQSEC2/BRAG1 may modulate postsynaptic density assembly through Ca2+-induced phase separation.
-
2025-08-22
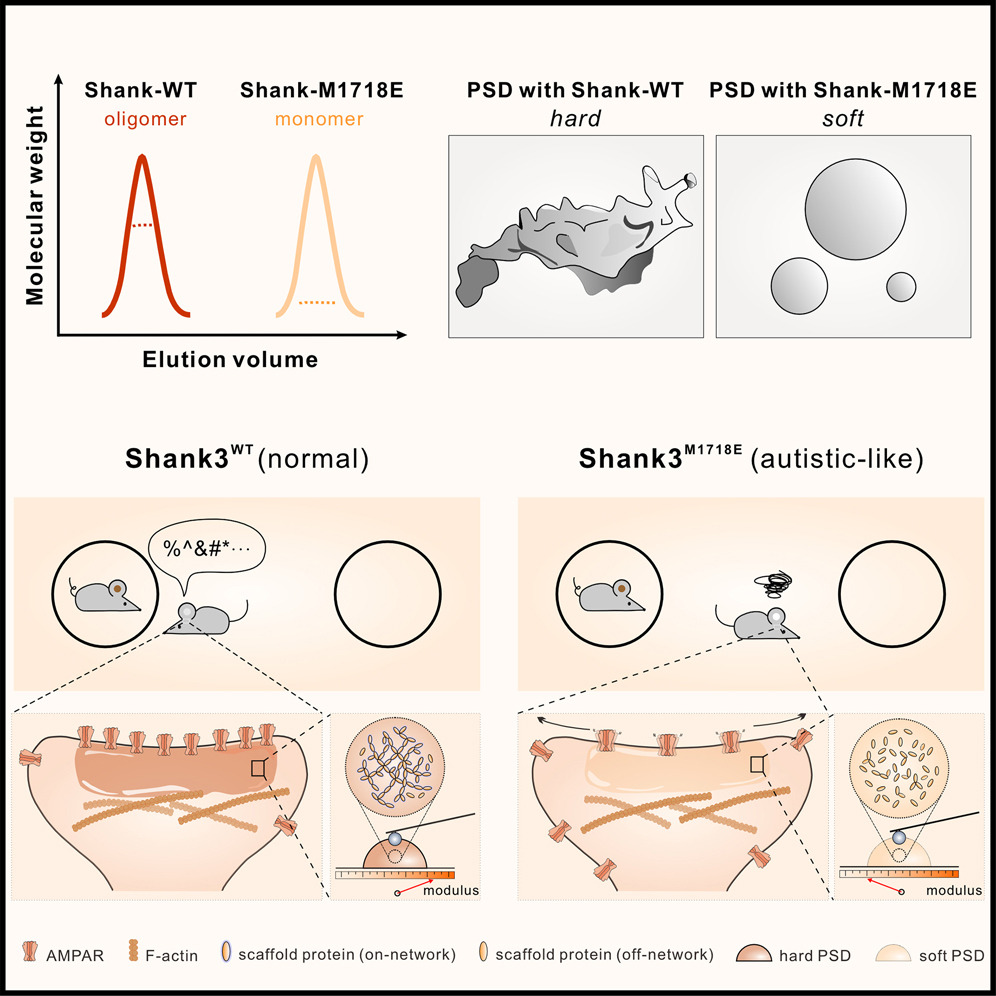
Shank3 oligomerization governs material properties of the postsynaptic density condensate and synaptic plasticity.
-
2025-08-21
Modulating synaptic glutamate receptors by targeting network nodes of the postsynaptic density condensate.
-
2025-08-19
Current practices in the study of biomolecular condensates: a community comment.
-
2025-06-10
Phase separation instead of binding strength determines target specificities of MAGUKs.